Applicative Programming
= functional programming 函数式编程
The three programming styles wewill cover in this book are applicative programming, recursion, and iteration
based on the idea that functions are data, just like symbols and lists are data, so one should be able to pass functions as inputs to other functions, and also return functions as values
These operators are all built from a primitive function known as FUNCALL
FUNCALL
(funcall #’cons ’a ’b) ⇒ (a . b)
Note that only ordinaryfunctions can be quoted with #’. Itis an error to quote a macro function or special function this way
> (setf fn #’cons)
#<Compiled-function CONS {6041410}>
> fn
#<Compiled-function CONS {6041410}>
> (type-of fn)
COMPILED-FUNCTION
> (funcall fn ’c ’d)
(C . D)
THE MAPCAR OPERATOR
Itapplies a function to each element of a list
> (mapcar#’square ’(1 2 3 4 5))
(1 4 9 16 25)
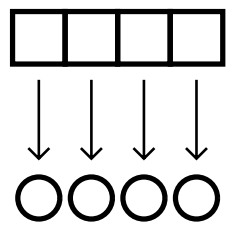
mutiple list
> (mapcar #’+ ’(1 2 3 4 5) ’(60 70 80 90 100))
(61 72 83 94 105)
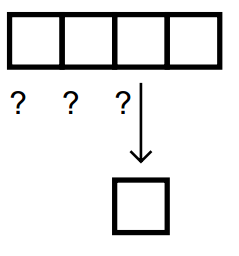
find-if
> (find-if #’(lambda (x) (> x 3))
’(2 4 6 7 8 9))
4
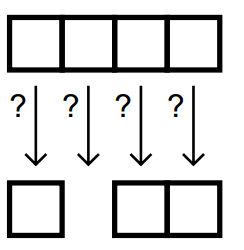
REMOVE-IFAND REMOVE-IF-NOT
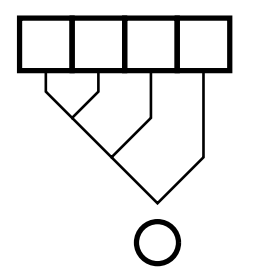
reduce
(reduce #’+ ’(1 2 3)) ⇒ 6
every
EVERY takes apredicate and a list as input. It returns T if there is no element that causes the predicate to return false.
> (every #’(lambda (x) (> x 0)) ’(1 2 3 4 5))
T
trace
...
fucntion
#’ is shorthand for the FUNCTION special function
WRITINGAN APPLICATIVE OPERATOR
(defun inalienable-rights (fn)
(funcall fn
’(life liberty and the pursuit of happiness)))
FUNCTIONSTHAT MAKE FUNCTIONS
(defun make-greater-than-predicate (n)
#’(lambda (x) (> x n)))